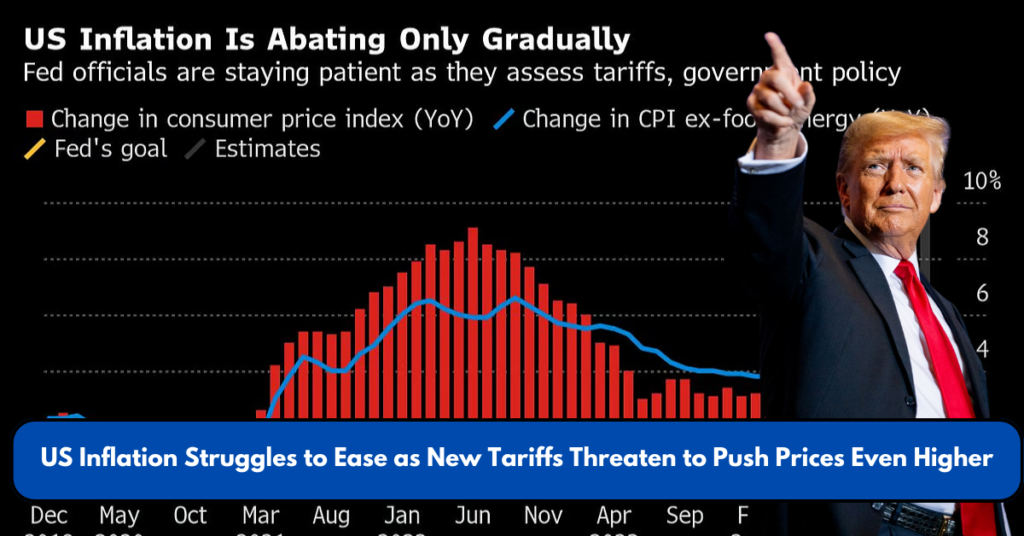
Washington, D.C. – March 2025 – The United States continues to struggle with persistent inflation, which remains above the Federal Reserve’s 2% target. At the same time, newly imposed tariffs by the Trump administration on major trading partners have raised concerns about further economic instability.
Inflation Pressures Remain Strong
The latest Consumer Price Index (CPI) data shows that inflation remains elevated, with rising costs in key sectors such as food, housing, and transportation. The Federal Reserve has spent months trying to bring inflation under control through interest rate hikes, but progress has been slow.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS.gov), consumer prices increased by 3.4% year-over-year, highlighting the ongoing challenge in reducing inflation to the Fed’s preferred level of 2%.
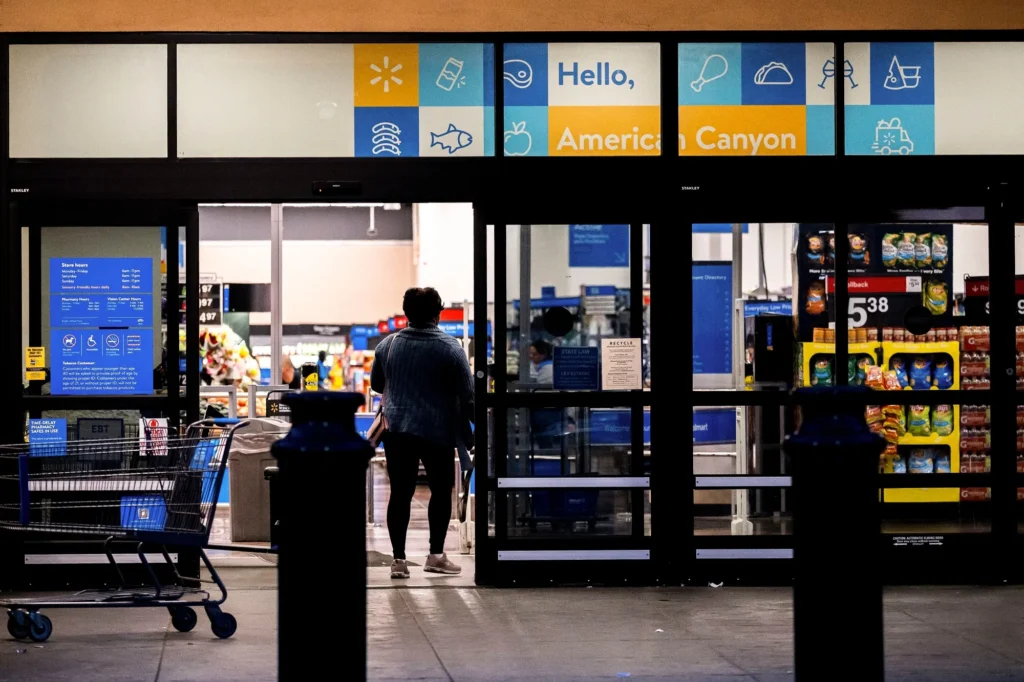

New Tariffs Add to Economic Uncertainty
On March 4, 2025, the Trump administration implemented a series of tariffs aimed at China, Canada, and Mexico. The tariffs include:
- Canada and Mexico: A 25% tariff on most imports, with a 10% tariff on Canadian energy products (New York Post).
- China: An increase in tariffs from 10% to 20% on imported Chinese goods.
These measures are part of an effort to address trade imbalances and combat drug trafficking, but they come with significant risks, including higher consumer prices and strained international trade relations.
How Tariffs Impact Inflation
Economists warn that tariffs on imports will drive up costs for businesses, which are likely to pass those costs onto consumers. This could further increase inflation at a time when the Federal Reserve is working to lower it.
Higher tariffs mean:
- Increased prices on everyday goods such as electronics, vehicles, and household products.
- Rising costs for US manufacturers who rely on foreign materials.
- Potential retaliatory tariffs from affected nations, increasing costs for American exports.
Financial markets have already reacted negatively, with stock indexes fluctuating as concerns grow over prolonged inflationary pressures and slowed economic growth.
International Response: Retaliatory Measures
In response to Trump’s tariffs, Canada and China have already announced countermeasures:
- Canada imposed a 25% tariff on $30 billion worth of U.S. goods and is considering expanding it to $125 billion in retaliation.
- China has introduced additional tariffs on U.S. agricultural products and is investigating certain U.S. companies for potential trade violations (New York Post).
These retaliatory actions add further uncertainty to an already volatile economic environment.
The Fed’s Dilemma: Interest Rates and Economic Growth
The Federal Reserve faces a complex challenge in balancing its fight against inflation with the risk of an economic slowdown. If tariffs continue to drive inflation higher, the Fed may have to delay interest rate cuts or even consider further rate hikes.
St. Louis Fed President Alberto Musalem emphasized that inflation expectations must remain anchored to avoid a situation where inflation becomes uncontrollable, potentially leading to a recession (Barron’s).

Recession Fears and Economic Stability
Some analysts warn that a combination of persistent inflation and rising tariffs could trigger what some are calling a “Trumpcession”—a recession driven by aggressive trade policies that disrupt global supply chains and increase prices domestically.
A report from MarketWatch (MarketWatch) noted that financial markets are bracing for inflationary shocks in the short term due to the administration’s economic policies.
What Comes Next?
With inflation remaining stubborn and new trade restrictions in place, the coming months will be crucial for U.S. economic stability. Key factors to watch include:
- The Federal Reserve’s next move: Will interest rates stay high for longer to control inflation?
- Trade negotiations: Will the U.S. negotiate new trade deals to ease tensions with Canada, China, and Mexico?
- Consumer spending trends: Will Americans reduce spending due to higher costs, slowing economic growth?
For now, businesses and consumers must prepare for potential price increases, while policymakers grapple with finding the right balance between protecting American industries and ensuring economic stability.
For more information on inflation, tariffs, and trade policies, visit:
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (CPI Report): www.bls.gov/cpi
- Federal Reserve Official Website: www.federalreserve.gov
- U.S. Trade Representative (Tariff Updates): www.ustr.gov
As the situation unfolds, the economic landscape remains uncertain, with both inflation and trade policies playing a pivotal role in shaping the U.S. economy in 2025 and beyond.
This article has been carefully fact-checked by our editorial team to ensure accuracy and eliminate any misleading information. We are committed to maintaining the highest standards of integrity in our content.

A senior at Yale-NUS College with interests in developmental and labour economics, as well as creative non-fiction and poetry. Currently, I’m studying as an Economics major and an Arts and Humanities minor (focusing on Creative Writing) with heavy involvement in the Singaporean journalism scene and involved in research on economic history and educational policy. I’m working as an author for SKC News, Yale-NUS’ student publication, as a writer for Wingspan, Yale-NUS’ alumni magazine, and as a tutor for the NUS Libraries Writer’s Centre. | Linkedin